Step 2 While Loops
Table of contents
What is a While-Loop?
For our eReader to read beyond the two first pages through the whole book, we need to continuously read and ask the reader to press ENTER for the next page. It is a typical case of while-loop, a structure that repeats a block of code while a condition is true. It involves the following elements:
Initialisation code the block of code that sets the initial condition
Condition the condition to continue iterating as long as it is true
Change code the block of code to change the condition
While-Loop Algorithm
1
2
3
Set the initial condition with [initialisation code];
then, iterate as long as the [condition] is true;
In each iteration, change the parameter of the condition with [change code]
While-Loop flow chart
While-Loop Python syntax
1
2
3
# initialisation code
while (condition):
# change code
Task 2.1 Move from If to While
Back to the eReader, we note that the while-loop is only a step away from the if already in the code.
- what is the initialisation code? The line that comes before the
if: Ask the user ‘For the next page, press ENTER:’ and store the answer in ‘action’. This line sets the ‘action’, which drives the condition that tells the computer to continue or to stop. - What is the change code? It is not there yet. Once we show the next page, we need to ask users whether they want to go to the next page or quit.
After integrating the while-loop, the eReader algorithm looks as follows. Note that we skip the elements that remain unchanged before and after.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
...
Ask the user 'For the next page, press ENTER:' and store the answer in 'action'
While user pressed ENTER (empty string)
Read the second page of the book and store it in the variable page_content
Show the user the second page of the book
Ask the user 'For the next page, press ENTER:' and store the answer in 'action'
...
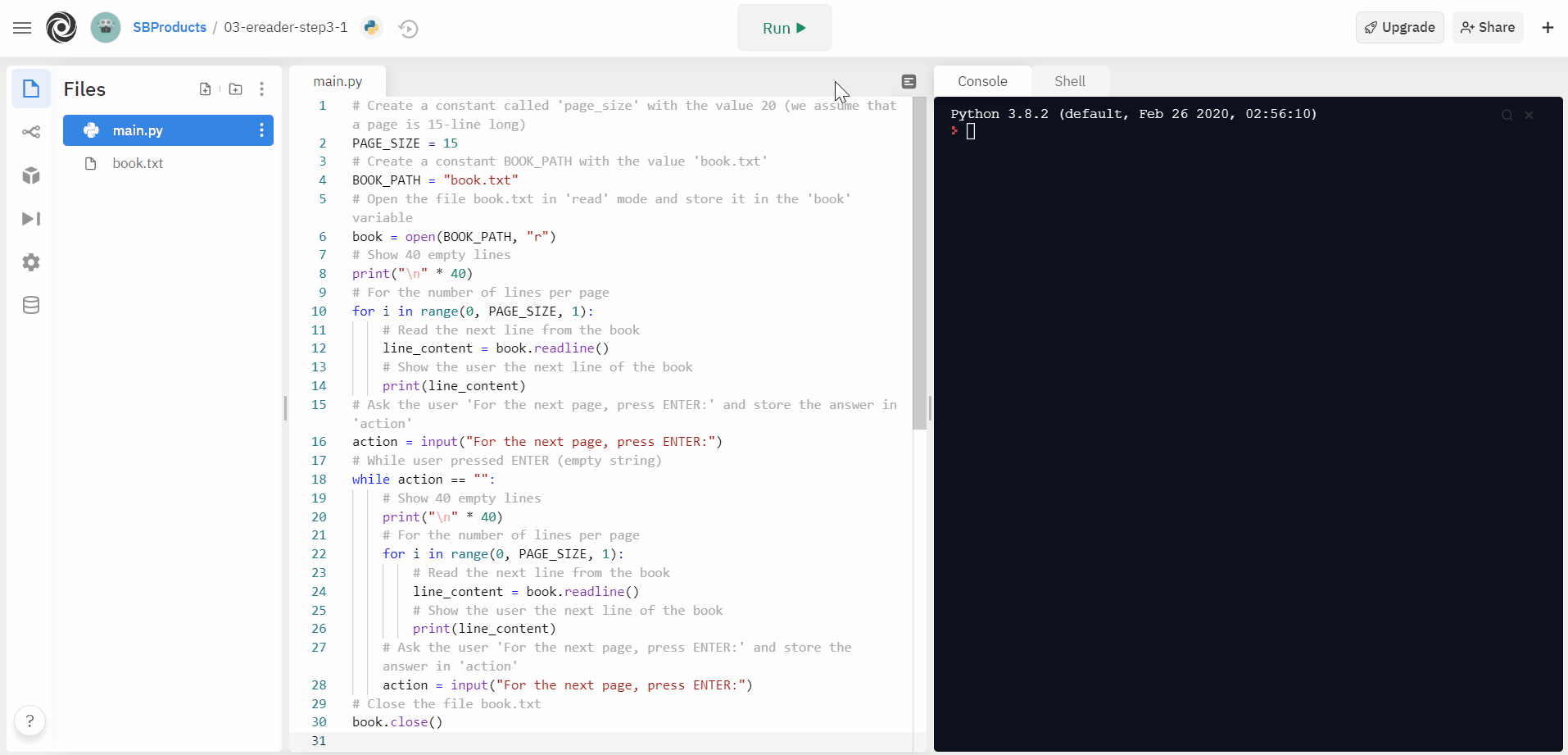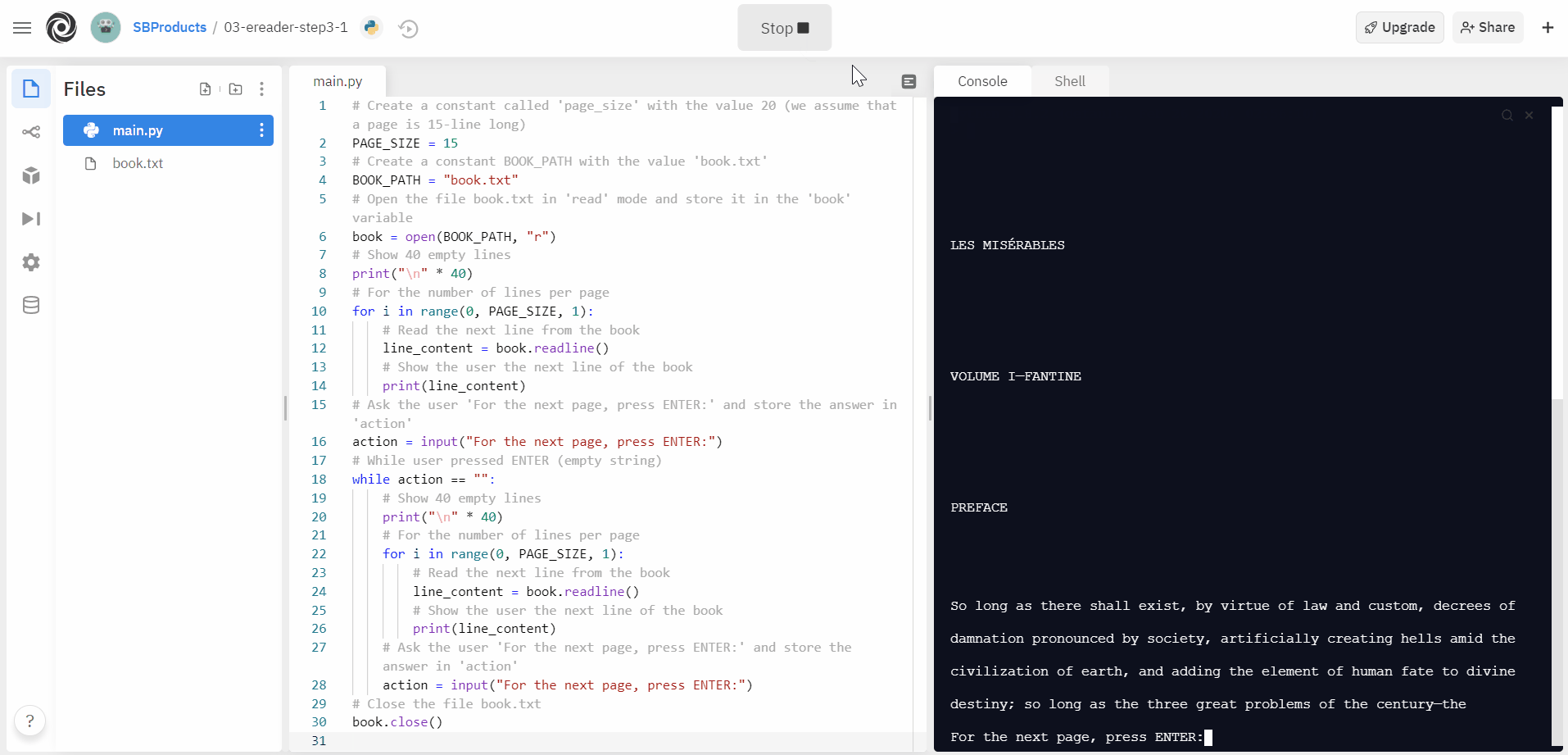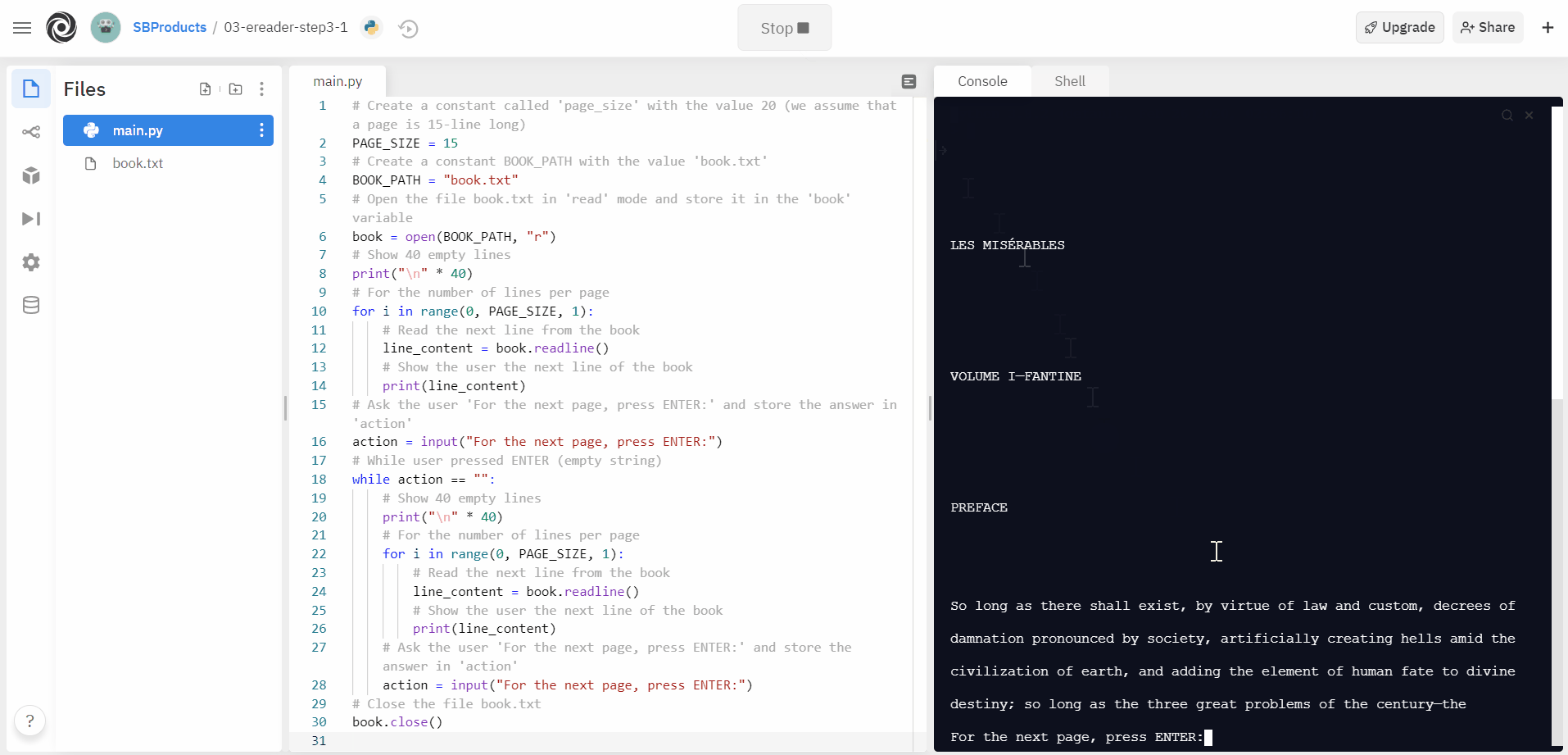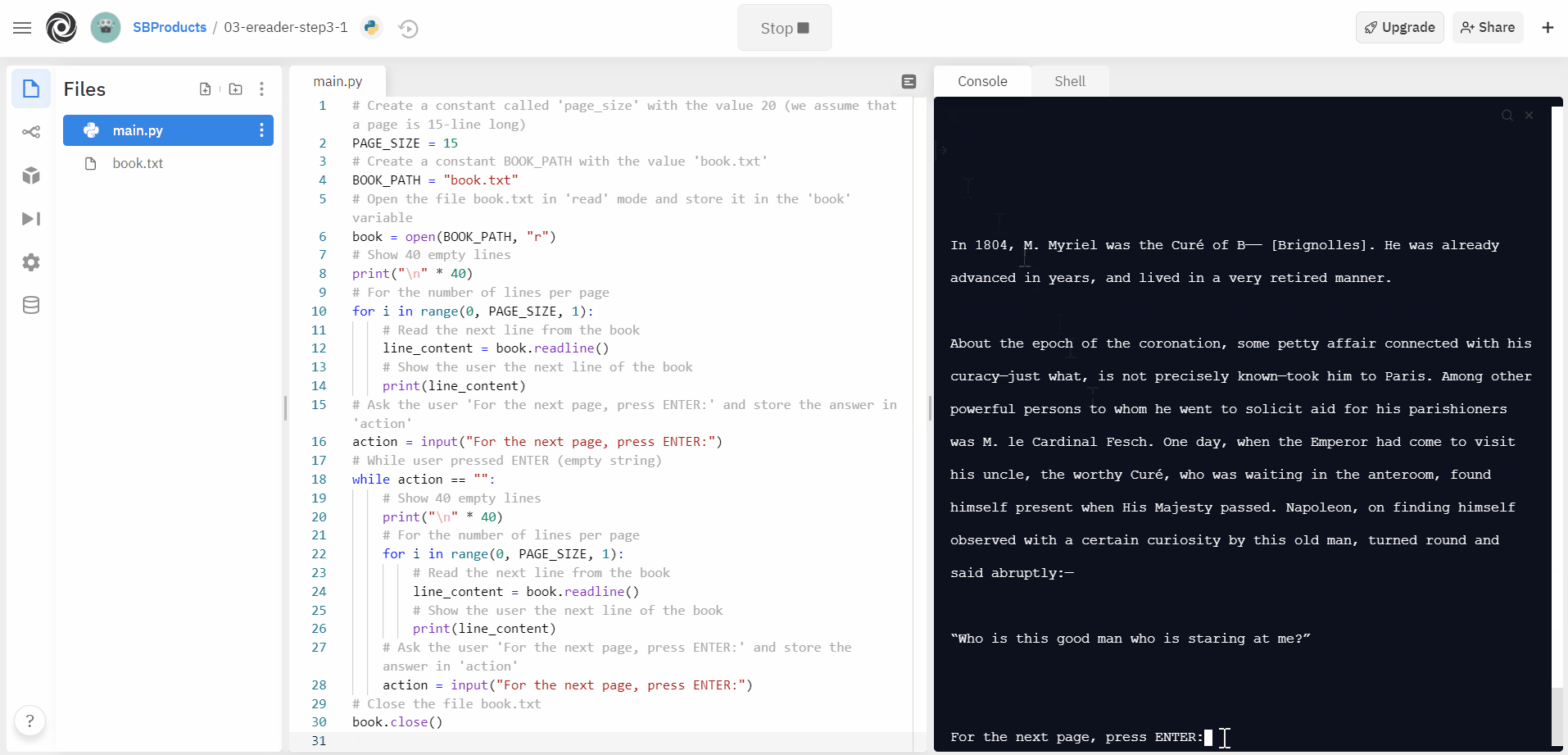
Make the two changes to the Python code and execute the program to see if it works as expected. As long as you press ENTER, the program should show the following page. Type in any character before pressing ENTER to stop the program. Why? Because the input will no longer equal ‘ENTER (empty string)’, thus the condition is false, which leads to leaving the while-loop and ending the programme.
While-loops are well suited when we do not know when to stop. This case is a good example, as we cannot know when the user will decide to continue or stop reading. In the next step we explore the For-Loop, another form of loops with a more structured condition.