File Formatting Guide
It is essential for preprocessing and model training that the datafiles you use are in the correct format. Here you can find how to correctly format your files to use in the Notebook.
File Formatting
The datafiles can contain the following elements:
Functional header: The first row from a file where each element tells you what kind of data can be found in the columns below.
Dysfunctional header: One or multiple rows at the beginning of the file that contain information that is not usable for the system.
Tracking columns: Columns that don’t contain raw data but that are essential for the program to function (e.g. ID, timestamp, label)
Preprocessing
For preprocessing, the datafiles should contain no header, a time column (oftentimes distinguishable by linear increments), and three data columns (X, Y and Z coördinates).
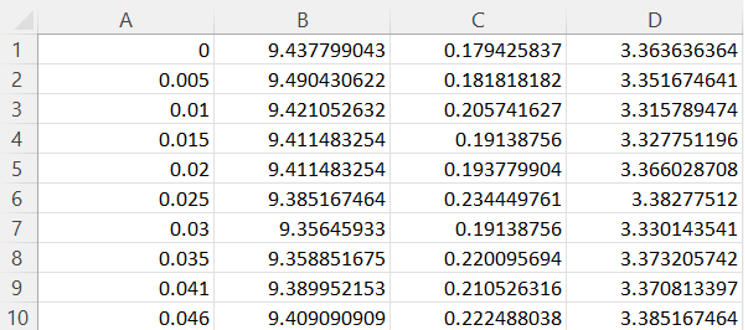
It should not matter if the file is .csv or .txt, as long as the data is separated by commas in the raw file. If you look at your files and find a file like the one below, there are a few things that should be fixed.
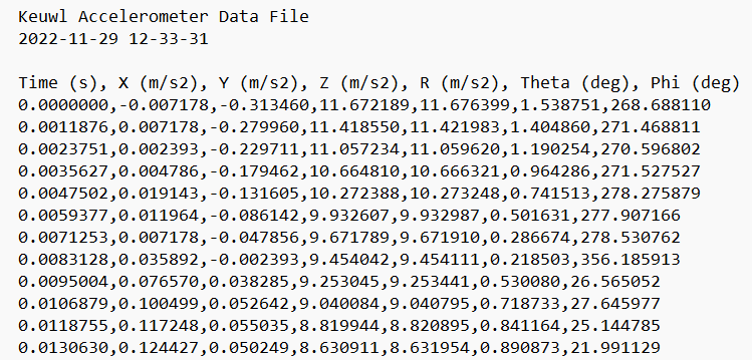
Firstly, notice that there are 4 dysfunctional header lines (including the line that starts with “Time (s)”). To remove this, you can set an extra parameter ‘n_to_check’ in the windowing function to the number of lines you want to skip: in this case 4.
Secondly, you cannot use the accelerometer and gyroscope data in the same file, but these should be added as separate files. For clarity, it would be preferable two have two files, one for the accelerometer and one for the gyroscope data, but it’s achievable with one file using the ‘start’ and ‘stop’ parameters. In calling the ‘pre.windowing’ function for the first time you set ‘start’ to 1 and ‘stop’ to 3, and for the second call you will set ‘start’ to 4 and ‘stop’ to 6.
The code for properly processing this data would therefore look as follows:
pre.windowing(input_file=[
r'same_data_file.txt', # Here you can enter your accelerometer file.
r'same_data_file.txt' # Here you can enter your gyroscope file.
],
video_file='Data/data-mok/GL010035_LRV.mp4', # Here you can enter the video corresponding to the datafiles.
start_offset = 0, # Here you can enter the start offset for this file.
stop_offset = 0, # Here you can enter the stop offset for this file.
skip_n_lines_at_start = 4, # Adjust this
video_offset = 0, # Here you can enter the video offset for this file
start = 1, # Adjust this
stop = 3, # Adjust this
size = frame_size, # This is the frame size, do not edit here.
offset = frame_offset,) # This is the frame offset, do not edit here.
pre.windowing(input_file=[
r'same_data_file.txt', # Here you can enter your accelerometer file.
r'same_data_file.txt' # Here you can enter your gyroscope file.
],
video_file='Data/data-mok/same_video_file.mp4', # Here you can enter the video corresponding to the datafiles.
start_offset = 0, # Here you can enter the start offset for this file.
stop_offset = 0, # Here you can enter the stop offset for this file.
skip_n_lines_at_start = 4, # Adjust this
video_offset = 0, # Here you can enter the video offset for this file
start = 4, # Adjust this
stop = 6, # Adjust this
size = frame_size, # This is the frame size, do not edit here.
offset = frame_offset,) # This is the frame offset, do not edit here.
Active learning
For active learning, the data should also be in the correct format. You can check this if you like, but the file should contain an ID, label (empty) and time-columns. The header contains the following:
ID,label,time,acc_x_min,acc_x_max,acc_x_avg,acc_x_std,acc_x_AUC,acc_x_pk,acc_x_cn,acc_x_pw,acc_y_min,acc_y_max,acc_y_avg,acc_y_std,acc_y_AUC,acc_y_pk,acc_y_cn,acc_y_pw,acc_z_min,acc_z_max,acc_z_avg,acc_z_std,acc_z_AUC,acc_z_pk,acc_z_cn,acc_z_pw
If you only added accelerometer data. If you added gyroscope data as well, the following should be there too:
,gyr_x_min,gyr_x_max,gyr_x_avg,gyr_x_std,gyr_x_AUC,gyr_x_pk,gyr_x_cn,gyr_x_pw,gyr_y_min,gyr_y_max,gyr_y_avg,gyr_y_std,gyr_y_AUC,gyr_y_pk,gyr_y_cn,gyr_y_pw,gyr_z_min,gyr_z_max,gyr_z_avg,gyr_z_std,gyr_z_AUC,gyr_z_pk,gyr_z_cn,gyr_z_pw
The file should be found under: ‘Preprocessed-data/{Product}/features_{Product}_scaled.csv’