Craft is an integral part of the design. In the research, we reviewed the development of craftsmanship in the past, looked at the innovation of new craftsmanship now, and imagined future trends under the DDW context.
RESEARCH INTRODUCTION
Research teams: Shicheng Huo, Xiangyu Li, Ruixuan Zhang
Research supervisor: Jacky Bourgeois
In this research, we will invest in craftsmanship in the DDW (Dutch design week). Craftsmanship is one
of the essential perspectives to looking at designs. How to use various crafts depends on designers and
their projects. The range of craftsmanship is wide. Especially in the recent ten years, the rise of new
media also influencing the design field. In the DDW, viewers can see unique craftsmanship, such as AI,
Mix realities, and Robotics. They can also see the innovation in traditional materials. Within the
research, we are planning to use multiple methods to uncover the development process, current trends,
and implementations of craftsmanship in design. Ultimately, we will convert our research into an
ethnography to conclude and share the research.


Design towards the future: sustainability, future social challenges. Focus more on the design for people's daily life.
Desk research
CRAFTS JOURNEY FROM 2012-2022
“DDW all began back in 1998. In that year the Vormegeversoverieg (a designers collaborative) organised the first Day of Design. Objective: introducing entrepreneurs to designers. The event, which took place annually in Eindhoven, attracted more interest each year and grew exponentially. The Day of Design became the Week of Design in 2002 and unltimatelt in 2005 it was renamed Dutch Design Week (DDW).”-DDW Website
2012
Enter a Brave New World
Social challenges, Food Design, Clothing
Keywords
General Environment Background: economic crisis. The sudden emptying of the purses raises enormous
questions about the survival of Dutch design in its current form. This conflict is most obvious in
the highly public restructuring of large institutions; At the same time, young independent
designers have lost several sources of funding, which have had disastrous consequences on the
infrastructure of Dutch design in terms of education, fabrication, and exhibition.




Traditional craftsmanship: traditional materials, facilitating day-to-day life, such as
furniture design, food and eating
Materials: plastic, textiles, wood
Machines: 3D
printings

2013
Now Future
Keywords
General Environment Background: still, economic crisis. Towards the future, what are the future's healthcare, food and lifestyle? Design with technologies involved more in DDW, especially the projects from technical universities. Designers seem to rethink how design can help with social challenges and facilitate people's daily life.



Materials: bio-materials
Machines: 3D printings
2014

UP
Recycling, Plastic waste
Keywords
This year designers focused more on sustainability and the future vision of society. Furthermore, the projects from DDW2014 give a lot of emphasis on the wastes and recycling issues.

Materials: recycled plastics
Machines: 3D printings
Methods: Speculative design
2015

What if...
Keywords
Concentrating on designing for the future, DDW 2015 generates people's thinking on what design can do to form the future, from people's daily life, including transportation, clothing, and eating. The role of designers is changing. They started to create interactions regarding social challenges and influences.

Materials: recycled materials, bio-materials
Machines: 3D printings
2016
The making of
Keywords
This was a year when minimalism was again in vogue, and designers began to rethink the use of
craftsmanship, materials, colors and shape in their designs. Many simple and delicate handicrafts
are on display at DDW. The collision of colors seems to be the mainstream, and combining different
colors creates an elegant, modern and delicate feeling. At the same time VR technology began to
rise, people began to use digital means to explore more design possibilities.

Materials:textiles, lighting
Machine:VR,CNC, laser cutting
2017
Stretch

, Bio-design experiences, lighting interaction
Keywords
Due to the evolvement of digitalization, interaction design, AI and installation art have been
emphasized and developed in recent years. Designers have begun to consider incorporating these new
technologies into the design process. As a result of DDW, a lot of conceptual design, experience
devices, and the designers, while exploring new technology, are demonstrating craftsmanship to the
public in a way that can be applied and, as a result, provoke more people to think and explore.
Technologies evloving in a high pase

Materials: recylced food waste,recycled plastic
Machines: VR, projection
2018
If not us, then who?

New media, Digitalized experience, Innovation
Keywords
This year, 3D printing technology has been widely used, and the breakthrough of 3D printing
provided a chance to print soft materials, metal or massive objects. Moreover, designers began to
explore a broader range of 3D printing fields and methods. Derivative design, VR and other
computation-based technologies have also begun to participate in the design process.

Materials:lighting,3D-printable metal,recycled PVC
Machine: 3D-printing,VR
Methods:Derivative
design
2019
If not now, then when?

Materials recycling, Sustainable building, Wood, Paint, Bionics, Natural interior environment
Keywords
This year, bionics became a trend in DDW, and there were more concerns about the generative
design, which brings DDW a more natural pattern. At the same time, carried on as previous two
years, this year still emphasizes sustainability, such as recycled material and bio-materials.
Materials:recycled materials,waste materials, bio-materials
Machine: 3D printing,
New era under COVID pandemic
2020
The New Intimacy

Keywords
General Environment Background: Covid pandemic
Due to the impact of COVID, 2020 DDW is an
online exhibition. People’s daily living space was limited due to the global pandemic. People have
reconsidered the relationship between nature and human beings. Many new materials are based on
bacteria and fungi for research and production. There are also many projects about food and eating
this year. More projects related to food and eating, such as edible paper made of food and
conceptual tableware.

Materials: Bio-plastic, Bio-textiles, Food based materials
Machines: 3D printings, AI drive
robot
Methods: Bacterial cellulose growed by microbes.
2021
The Greater Number

Keywords
General Environment Background: During the pandemic. The world was still under the effect of COVID.
And there was a rising awareness among designers about healthcare and people's well-being that
are related to day-to-day life, such as textiles, food and mobility.
Materials: Bio-textiles, Food based material
Machines: 3D printings, robotics
Field research

2022
Get set
As the first that after the COVID pandemic, life seems back to normal. People finally get to step out of their rooms, feel and interact with the natural world again. This year's DDW generates a lot of thinking about the relationship between humans and non-humans, as well as improving people's life quality by innovative technologies and methods. Lots of new materials experimentations are also exhibited in the design week.
Materials: Recycled materials, bio-based material,data
Machines: 3D printings, robotics, VR,
electronics
Methods: Bio-design, AI technologies, traditional crafts
Neo-craftsmanships are reshaping the manufacturing system to be more sustainable. They also move towards consumer behaviour change.

Neo-craftsmanship is changing over time. Environmental and other factors are also talking in considerations besides human factors.


An end cycle means a new start. Designers‘ ingenuity empowers this to happen.

Neo-craftsmanships bring new channels for forming relationships by visualizing and
materializing invisible components.






Technologies and ideas change everyday experience.


Neo-craftsmanships are redefining attributes of good design. It does not have to have perfect edges, well-polished surfaces, or be trendy. Designers are seeking a more natural and connected way to produce their designs.





Crafting with intangible materials (e.g., data and machines) fills the gap between human and non-human awareness.



Craftsmanship is not only about functionalities but also about the experience.




Designers extend the boundaries of using materials.




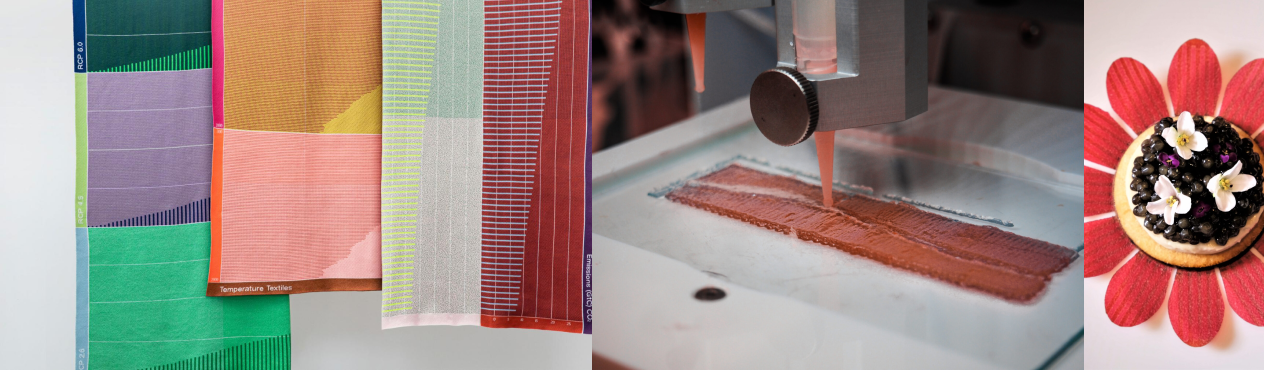
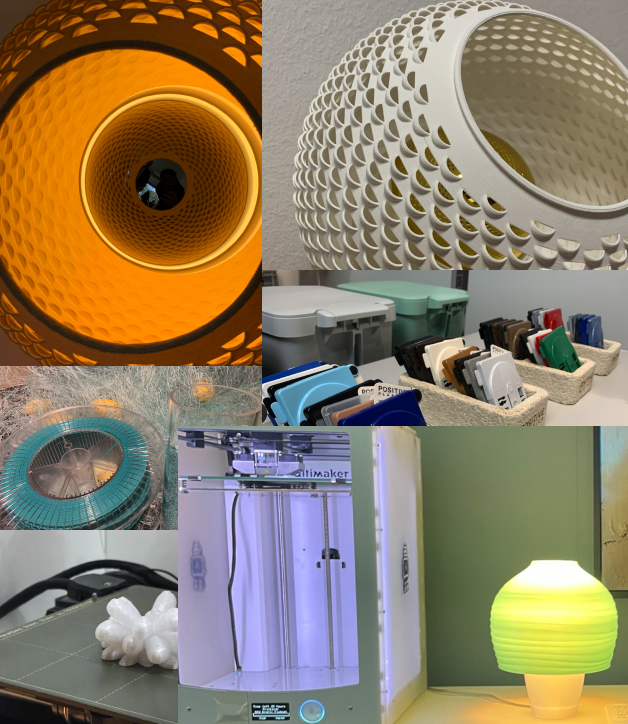
Project highlights:
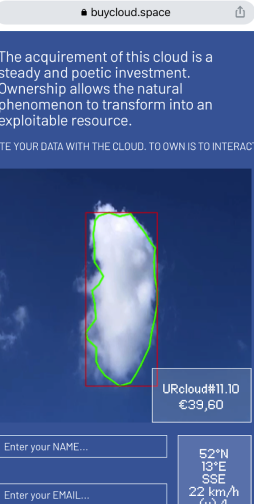




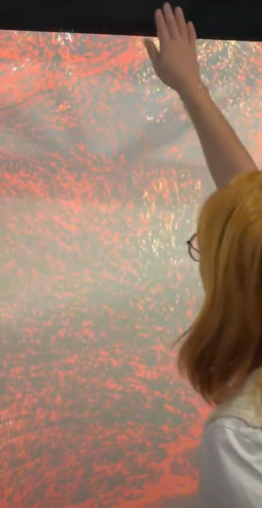

OUR ANSWER TO THE RESEARCH QUESTIONS
In the past decade of DDW, we saw the fast evolvement of craftmanship regarding materials, machines and methods. Designers started to adopt more and more material possibilities and employ new technologies to generate design ideas. Technological development has been influencing designs in recent decades. Designers are rethinking the attributes of designs.
RETHINK
The past decade's breakthrough in materials and technologies brings unlimited possibilities and
means for designers. By using different design techniques, designers tried to tackle social
challenges, evoke people's thinking, and provide potential solutions towards the future. We can
see new practices in the design week, such as using old, unnoticed materials to create a new design
or using new materials or technologies to improve the current industry.
REDEFINE
With the digitalisation trend, many designers from DDW focus on intangible craftsmanship to create new experiences and interactions, and some of them combine tangible and intangible materials. Designers are actively exploring the boundaries of materials and technologies in their practices. Using the same technologies, methods, purposes, or processes may produce different results.
REMAKE
The role of designers is beyond thinking about users' needs and functionalities. New technologies, materials and methods provide tremendous potentials for designers to dive deep into their concepts. Nowadays, designers pay more attention to systems, relationships, non-human interactions, environment and other related factors of a piece of design. Neo-craftsmanship is a new challenge for designers, but it also is a new chance.
REDIRECTING
FUTURE
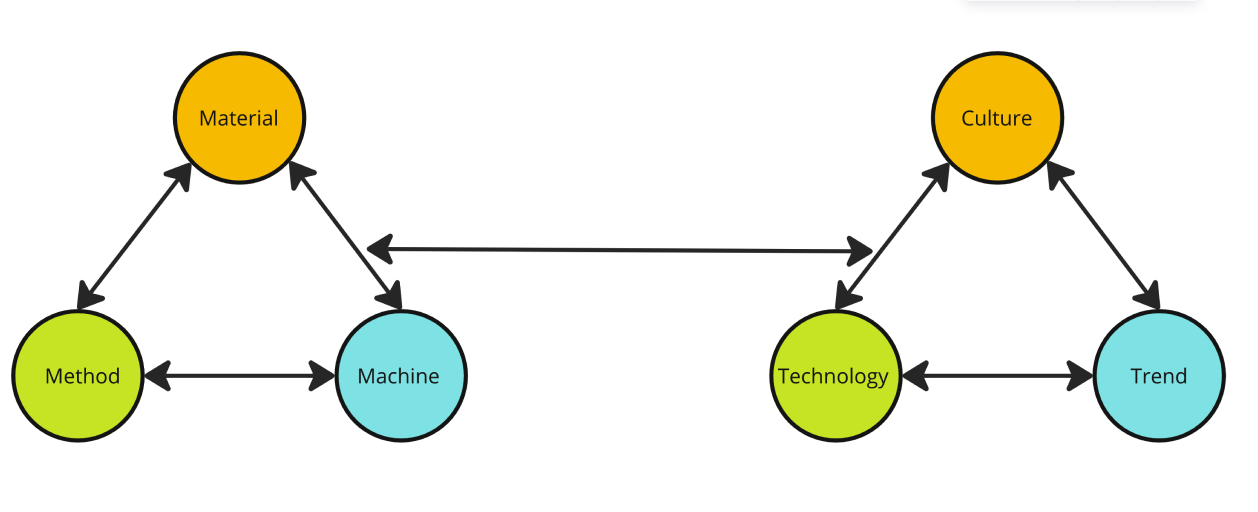
Craftsmanship involves traditions, design thinking, creativities, innovation, materials and
cultures. Making a good balance between these attributes and achieving high qualities is how people
generally understand the traditional craft. It is different from perfect manufacturing in the modern
era. However, the rise of neo-craftsmanship provides a new perspective on craftsmanship. It combines
aesthetics, practicality, functionality, thinking and technologies. Neo-craftsmanship is a merging
process driven by new technologies and developments of methods. Neo-craftsmanship is also led by new
design thinking, which considers more about our surroundings.
Craftsmanship is different from artwork and products. Artwork is the expression of the artist's self-spiritual pursuit, and standardized products are a production based on user needs. The neo-craftsmanships are in between, which express designers' stories and present unique products with practicality and functionality. The function is not limited by using purpose. It contains messages that designers want to deliver. There is still no solid conclusion on how to define neo-craftsmanship in the future because technology is constantly developing, and the environment is constantly changing. Nevertheless, in our view, neo-craftsmanship is the best way for designers and artists to show their vision for the future and discuss their thinking with people.